Facial recognition and iris recognition are two leading biometric authentication technologies, each offering unique security advantages. Facial recognition provides fast and convenient identity verification by analyzing facial features, while iris recognition ensures higher accuracy and security through the unique patterns of the iris. This article compares their principles, applications, strengths, and limitations, evaluating which technology offers greater security and exploring their future potential in advanced authentication systems.
This article compare iris vs facial recognition: how they work, best uses, and security levels. Get key insights and FAQs to pick the right solution.
What Are Facial Recognition and Iris Recognition?
التعرف على الوجه
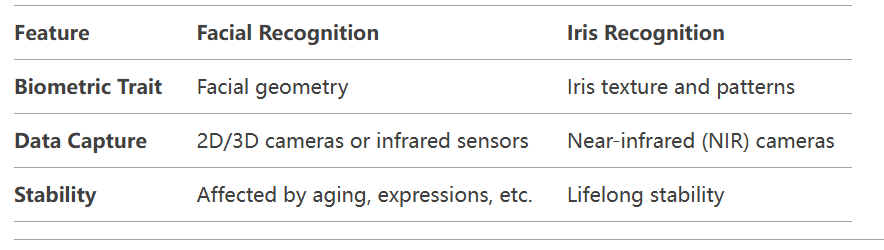
Facial recognition is a biometric technology that identifies individuals by analyzing unique facial features such as the distance between the eyes, nose shape, and jawline. It uses AI algorithms to map and match these features against stored templates.
التعرف على قزحية العين
التعرف على قزحية العين is a biometric method that authenticates individuals by scanning the intricate patterns of the iris—the colored ring around the pupil. These patterns, including crypts, furrows, and freckles, are unique to each person and remain unchanged throughout life.
Understanding Facial Recognition
How Facial Recognition Works
Facial recognition uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to map facial features such as the distance between the eyes, nose shape, and jawline. Advanced systems employ 3D imaging or infrared sensors to improve accuracy in low-light conditions.
Key Applications
1. Device Unlocking
Apple’s Face ID, Android Face Unlock.
2. Surveillance
Real-time identification in public spaces.
3. Border Control
Automated eGates at airports.
4. Retail & Banking
Contactless payments and fraud prevention.
Pros and Cons
Understanding Iris Recognition
How Iris Recognition Works
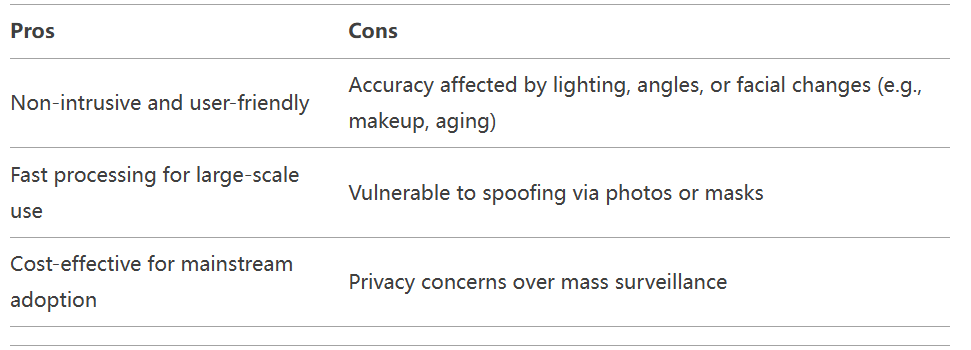
التعرف على قزحية العين uses near-infrared (NIR) cameras to capture the unique patterns in the iris, such as crypts, furrows, and freckles. These patterns remain stable throughout life, enabling highly accurate identification.
Key Applications
1. High-Security Facilities
Government buildings, research labs.
2. Healthcare
Secure access to patient records.
3. Border Security
Used in UAE and India for immigration checks.
4. Military & Defense
Restricted area access.
Pros and Cons
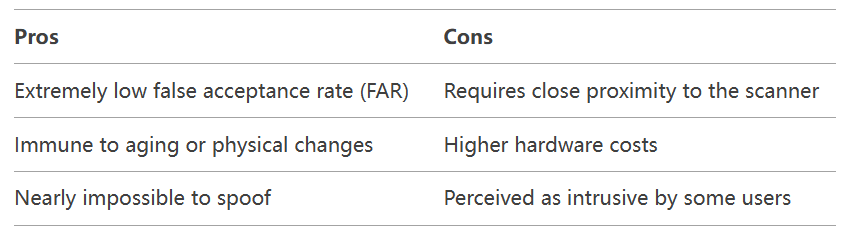
Facial Recognition vs Iris Recognition: Key Differences
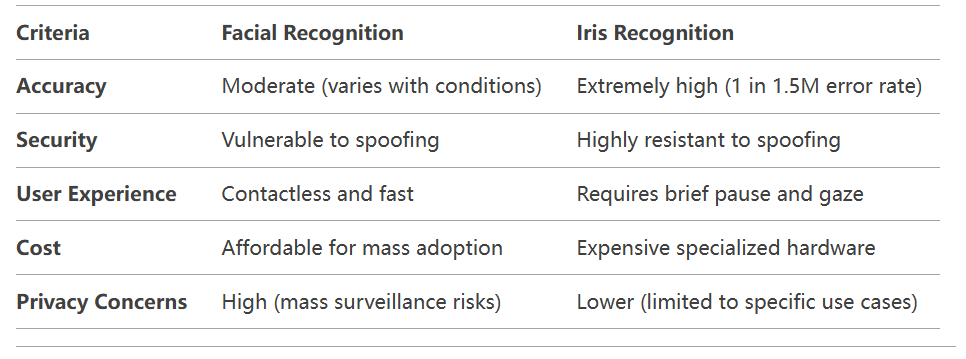
Future Prospects
التعرف على الوجه
Advancements in AI and 3D imaging will improve accuracy and anti-spoofing capabilities. However, stricter privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR) may limit its adoption in public spaces.
التعرف على قزحية العين
Miniaturization of hardware could integrate iris scanners into smartphones and wearables. Its use in healthcare and finance is expected to grow due to its unmatched security.
خاتمة
The debate between التعرف على قزحية العين و التعرف على الوجه hinges on the trade-off between security, convenienceو cost. Here’s a concise recap:
Facial recognition
excels in user-friendliness و mainstream adoption, making it ideal for everyday applications like smartphone unlocking and retail. However, its vulnerabilities to spoofing and environmental factors limit its use in high-security scenarios.
التعرف على قزحية العين
offers unmatched accuracy و fraud resistance, suited for critical environments like government facilities or healthcare. Its higher costs and need for user cooperation, however, hinder widespread consumer use.
Security verdict
Iris recognition is inherently more secure due to its reliance on lifelong, unalterable biological traits. For most users, التعرف على الوجه strikes a practical balance, but industries prioritizing airtight security should opt for التعرف على قزحية العين or hybrid systems.
As biometric technology evolves, combining both methods could deliver seamless yet ironclad authentication. Your choice ultimately depends on prioritizing convenience or security—or embracing the best of both worlds.
FAQs
Facial recognition analyzes facial features, while iris recognition scans the unique patterns in the colored part of the eye.
Iris recognition is inherently more secure due to its reliance on unique, stable biological patterns that are nearly impossible to replicate.
Yes, systems using infrared (IR) or 3D depth sensors (e.g., iPhone Face ID) can operate in low-light conditions.
Yes—modern iris scanners use non-invasive near-infrared light, posing no risk to the eyes.
Facial recognition has faced criticism for racial/gender bias, while iris recognition is less affected due to its focus on texture, not skin tone.


