This article covers iris recognition, its functionality, and its impact across industries. You’ll learn why it’s a top biometric security solution, with a FAQ section for key insights.
Key Features of Iris Recognition
1.Uniqueness
Each iris contains over 200 distinct features, including crypts, furrows, and freckles.
Even identical twins have irises with different patterns.
2.Non-Invasive and Contactless
Unlike fingerprint scanning, iris recognition works from a distance (up to 1 meter) using near-infrared cameras, ensuring hygiene and convenience.
3.High Accuracy
With a decidability index (d-prime) exceeding 11 and false match rates as low as 1 in 1.5 million, it outperforms most biometric systems.
4.Adaptability
Advanced algorithms, like John Daugman’s IrisCode, normalize iris images into polar coordinates to account for pupil dilation and lighting variations.
5.Anti-Spoofing Capabilities
Detects live irises by analyzing texture and pupillary reflexes, thwarting attempts using photos or artificial lenses.
How Iris Recognition Works
The process involves four stages:
1.Image Acquisition
Near-infrared cameras capture high-resolution iris images, even in low-light conditions. Modern systems allow “iris-on-the-move” scanning for seamless user experiences.
2.Preprocessing
Localization
Algorithms detect the iris boundaries using circular edge detectors.
Rubbersheet Model
Converts the iris ring into a normalized polar coordinate system to account for size and rotational variances.
3.Feature Extraction
Gabor Filters
Encode texture details into binary IrisCodes (2,048 bits per iris).
Machine Learning
Advanced methods like ConvNeXt-tiny neural networks use triplet mining to enhance feature discrimination.
4.Matching
The Hamming distance compares IrisCodes, with scores below a threshold confirming identity. Open-source tools like HDBIF and CRYPTS optimize matching by focusing on human-interpretable features.
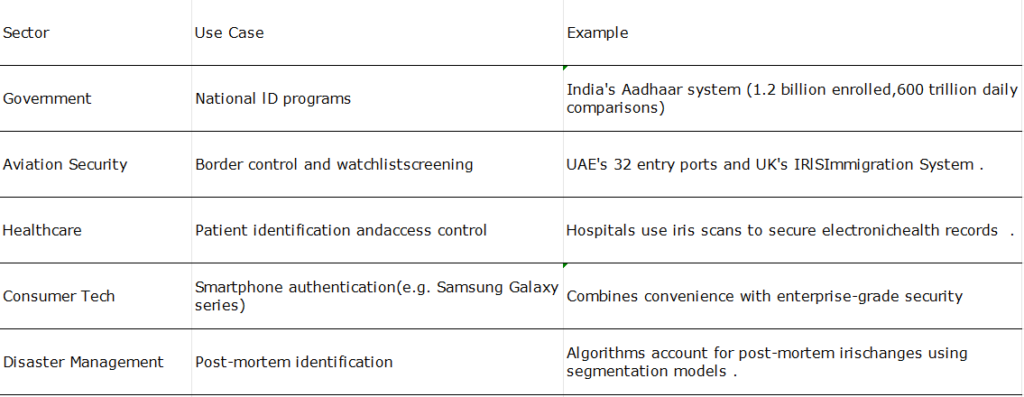
Real-World Applications
Future Prospects
3D Iris Recognition
Emerging 3D sensors capture iris curvature for enhanced accuracy, reducing errors from angular variations.
AI-Driven Advancements
Neural networks like TripletNN improve matching speed and adaptability across diverse demographics
IoT Integration
Smart homes and vehicles may adopt iris scanners for personalized automation
Ethical AI Frameworks
Addressing biases in datasets to ensure equitable performance across ethnic groups
FAQs
Yes. Near-infrared light is harmless, and systems include safety sensors to prevent accidental exposure.
Most systems accommodate clear lenses, but tinted or patterned lenses may require removal.
Weatherproof cameras and rust-resistant materials (e.g., aluminum) ensure reliability in rain or snow.
Iris patterns remain stable, but severe trauma may require re-enrollment. Backup authentication methods are recommended.
IrisCodes are encrypted and cannot be reverse-engineered to recreate iris images, ensuring privacy.
Conclusion
Iris recognition stands at the forefront of biometric innovation, offering unmatched security and versatility. From safeguarding national borders to enabling seamless smartphone access, its applications are vast and growing. As AI and 3D imaging evolve, this technology will redefine identity verification, making it faster, more inclusive, and virtually foolproof.

