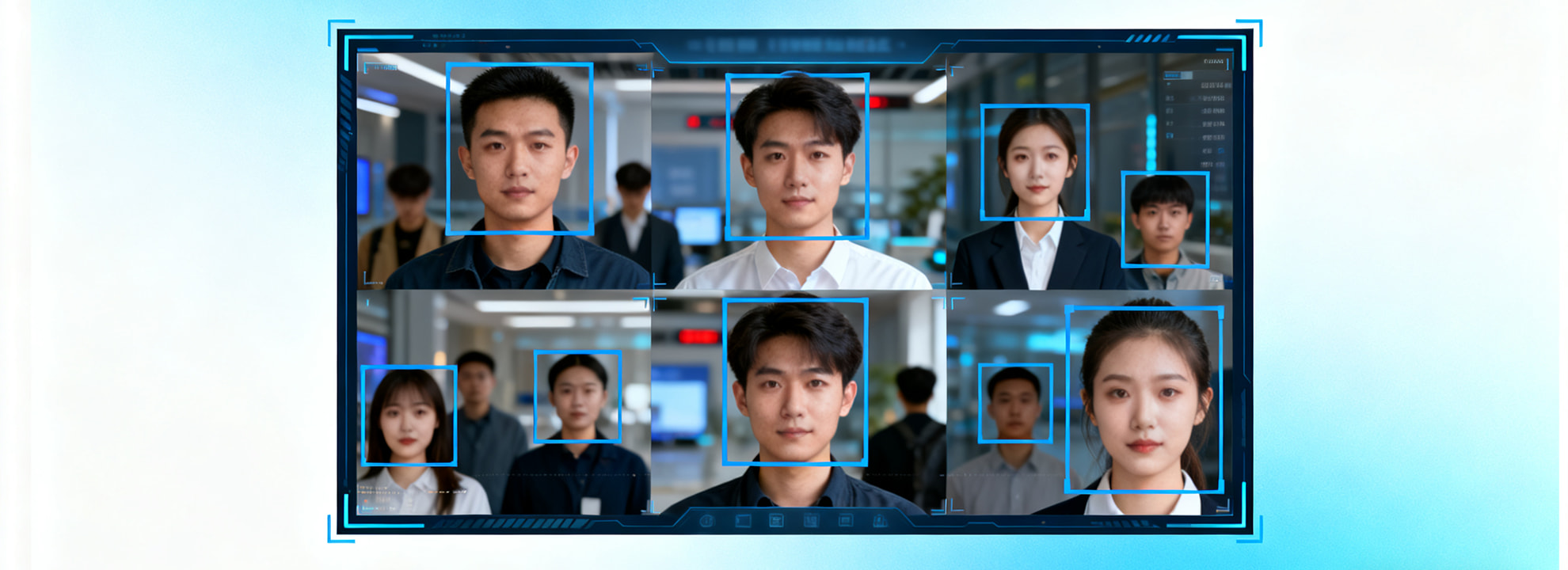
Reconocimiento facial, also known as facial recognition, is a biometric technology that identifies or verifies a person by analyzing unique facial features. With advancements in AI facial technology, deep learning, and computer vision, face recognition systems have become faster, more accurate, and widely used across modern security, identity verification, and access control applications.
From unlocking smartphones to securing airports and office buildings, facial recognition has evolved into one of the most efficient and contactless methods for authentication.
How Face Recognition Works
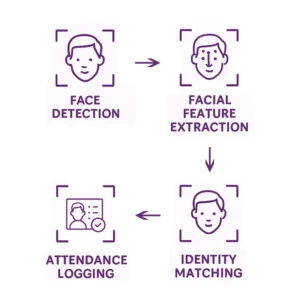
Face recognition technology operates through several stages, each powered by AI and data processing algorithms. Understanding these steps helps explain why modern facial technology is both fast and highly reliable.
1. Face Detection
The system scans the environment—via camera or sensor—to detect a human face. AI models locate facial regions, even in challenging conditions such as low light, large crowds, or movement.
2. Feature Extraction
Once a face is detected, the system maps key facial landmarks: eye distance, nose shape, jawline, cheekbones, and other unique characteristics. These details form a mathematical face template, not an actual image.
3. Face Matching
The extracted template is compared with stored templates in the system database. Advanced algorithms calculate similarity scores to determine whether there is a match.
4. Authentication or Identification
If similarity meets the threshold, the person is verified or identified.
Verification (1:1): “Are you who you claim to be?”
Identification (1:N): “Who is this person in the database?”
Why Face Recognition Is Widely Used
As digital transformation accelerates, organizations prefer facial recognition for its speed, convenience, and enhanced security. Compared to traditional authentication methods—such as cards, PIN codes, or fingerprints—face recognition is entirely contactless, faster, and more hygienic.
Accurate and Efficient
AI-powered systems achieve extremely high recognition accuracy, even with masks, hats, or glasses.
Contactless and Hygienic
Facial technology requires no physical touch, reducing contamination and improving user flow.
Fast Response for High-Traffic Scenarios
Modern face recognition can process thousands of users per hour, making it ideal for airports, metro stations, factories, and office buildings.
Difficult to Forge
Advanced systems include anti-spoofing features to prevent photos, masks, and video attacks.
Key Features of Modern Facial Recognition Technology
High-Speed Processing
AI algorithms and deep learning allow recognition within milliseconds, enabling real-time identification and verification. Fast processing improves efficiency and ensures smooth pedestrian flow for access control in offices, airports, and public facilities.
Strong Anti-Spoofing Security
Infrared imaging, 3D sensing, and liveness detection prevent spoofing attempts using photos, videos, or masks. This ensures secure biometric authentication for banks, government buildings, and data centers.
Wide Environmental Adaptability
Face recognition works reliably under various conditions—low light, backlight, harsh sunlight, and crowded areas. Infrared sensors and AI enhance image capture for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Multi-Scenario Integration
Devices integrate with access control, attendance systems, visitor management, payment terminals, and IoT platforms, streamlining operations while improving security across multiple use cases.
Scalable Database Capability
Supports storage and matching of thousands to millions of facial templates, enabling reliable identification even in large-scale environments such as airports, stadiums, and smart city security networks.
Applications of Face Recognition
Access Control – Offices, factories, residential buildings, and turnstile gates.
Time Attendance Systems – Prevents buddy-punching, streamlines employee tracking.
Public Transportation – Airports, metro stations, and bus terminals for identity checks and ticketing.
Retail & Payment Solutions – Face-pay systems for fast, secure transactions.
Healthcare & Education – Patient identification and student management.
Government Services – Border control, ID registration, and secure facility access.
Face Recognition vs Other Biometrics
| Tecnología | Sin contacto | Velocidad | Exactitud | Security Level | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reconocimiento Facial | Sí | Very Fast | Alto | Alto | Access control, attendance, transportation |
| دقة | No | Rápido | Alto | Medio | Banking, government ID |
| Reconocimiento de iris | Sí | Medio | Very High | Very High | Airports, high-security zones |
| Vena de palma | Sí | Rápido | Very High | Very High | Healthcare, high-security identity verification |
Safety and Privacy Considerations
Modern facial recognition uses encrypted templates instead of real images, ensuring privacy. Combined with anti-spoofing, AI liveness detection, and secure data storage, face recognition is highly secure against identity fraud.
Conclusión
Face recognition has become a fast, accurate, and contactless solution for identity verification, access control, and attendance management. With its advanced AI algorithms, strong anti-spoofing measures, and integration with multiple systems, facial recognition technology continues to redefine modern security, streamline operations, and improve user experience across industries.
Contáctenos
We would love to speak with you.
Feel free to reach out using the below details.