n the age of intelligent access and digital security, authentification biométrique is revolutionizing how we identify individuals. Among the most advanced technologies available today are la reconnaissance faciale and reconnaissance de l'iris. But the question remains: facial recognition or iris recognition—which is better for your needs? This article dives deep into the comparison of these two methods to help you choose the right solution.
What Is Facial Recognition?
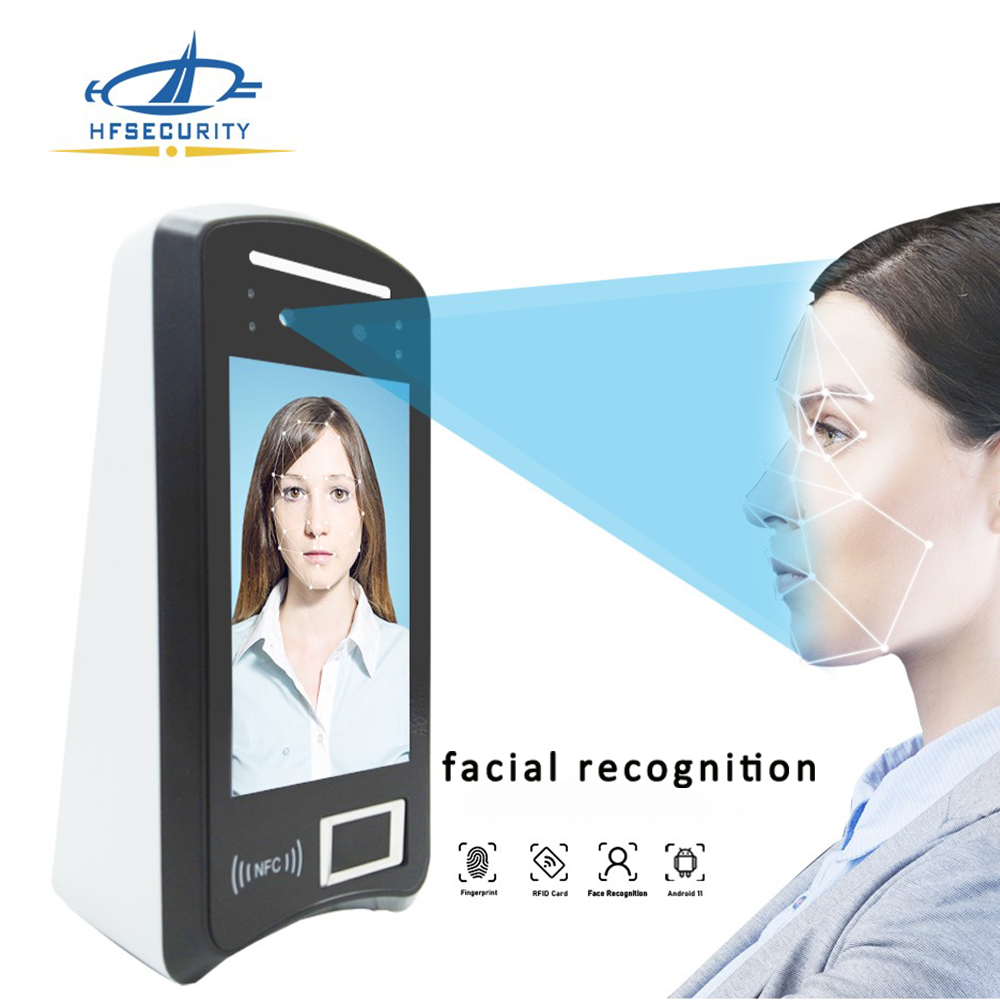
Facial recognition is a cutting-edge biometric identification technology that uses artificial intelligence to recognize and verify human identities based on facial features. Unlike traditional methods that require physical contact, facial recognition is entirely contactless, making it ideal for modern, hygienic, and automated systems.
This technology works by capturing a digital image or real-time video of a person’s face. It then analyzes distinct facial landmarks—such as the distance between the eyes, the shape of the nose, cheekbone structure, and jawline contour—using advanced machine learning algorithms. The extracted data is converted into a facial biometric template, which is then compared with a stored database for authentication or verification.
What Is Iris Recognition?
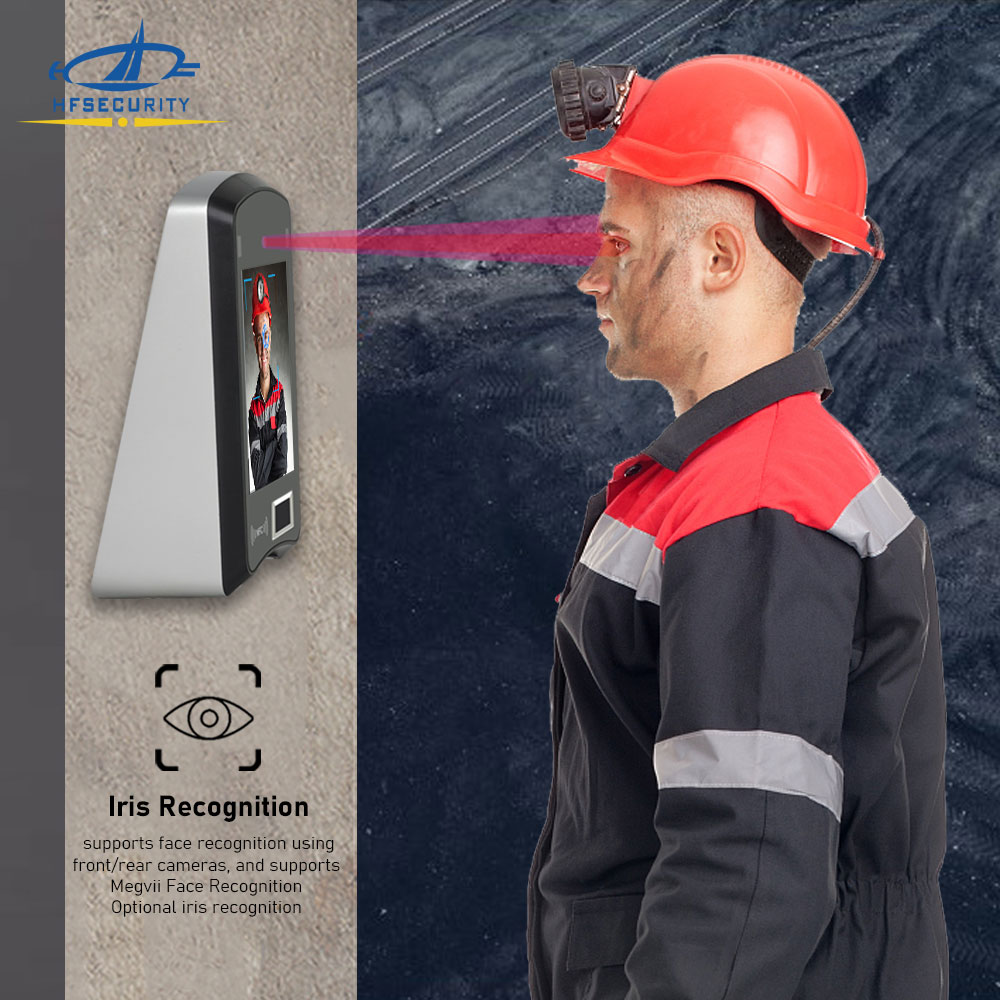
Reconnaissance de l'iris is a highly secure and precise biometric identification method that captures and analyzes the unique patterns in a person’s iris—the colored ring surrounding the pupil. These patterns are distinctive for every individual, even between identical twins or left vs. right eyes, making iris recognition one of the most accurate biometrics available today.
This technology uses near-infrared (NIR) imaging to illuminate the eye and capture high-contrast images of the iris, even in low-light or outdoor conditions. The system then converts the iris structure into a digital code, known as an iris template, and matches it against pre-registered templates to verify identity.
Advantages of Facial and Iris Recognition
Advantages of Facial Recognition Technology
Fast Processing Speed
Facial recognition systems offer near-instant identification and verification, typically within one second. This makes them ideal for locations with high foot traffic such as airports, metro stations, and office buildings.Contactless and Convenient
Users do not need to touch any surface. Facial recognition works at a distance, making it more hygienic and comfortable, especially in public or shared environments.Remote Identity Verification
The technology supports secure remote authentication, making it suitable for mobile banking, eKYC processes, and online account verification.High Security with Liveness Detection
Advanced systems include liveness detection that can prevent spoofing attempts using printed photos, videos, or masks. This increases the reliability of facial biometric authentication.Seamless System Integration
Facial recognition can be easily integrated with access control systems, attendance tracking, surveillance networks, and smart city platforms. It offers scalable deployment options across industries.
Advantages of Iris Recognition Technology
Extremely High Accuracy
Iris recognition offers exceptional precision with false acceptance rates as low as 1 in 1.2 million. It’s one of the most reliable biometric technologies, suitable for high-security applications.Performs Well in Low Light
Using near-infrared imaging, iris scanners can capture clear patterns even in dark or low-light environments. This ensures consistent performance regardless of lighting conditions.Highly Secure and Difficult to Forge
The iris is an internal organ, protected by the eye and nearly impossible to replicate or manipulate. This makes iris authentication far more secure than surface biometrics like fingerprints.Biometric Stability Over Time
Iris patterns remain stable throughout a person’s lifetime. Unlike facial features or fingerprints that may change due to age or injury, iris data remains consistent.Ideal for Government and Institutional Use
Because of its accuracy and stability, iris recognition is widely used in national ID systems, e-passports, border control, military access, and hospital patient identification systems.
Facial Recognition vs. Iris Recognition: A Detailed Comparison
| Feature | Reconnaissance faciale | Nhận dạng mống mắt |
|---|---|---|
| Contactless | Oui | Oui |
| Précision | Moderate to High (95–98%) | Very High (up to 99.9%) |
| Vitesse | Extremely fast (real-time) | Slightly slower due to close-up requirement |
| Lighting Sensitivity | Can be affected by poor lighting | Performs well in low light with infrared |
| User Experience | More convenient, user-friendly | Less convenient, requires closer distance |
| Sécurité | Susceptible to spoofing without liveness | Harder to spoof due to unique iris patterns |
| Cost of Implementation | Lower | Higher due to specialized cameras |
How to Choose Between Facial Recognition or Iris Recognition?
Choosing between facial recognition or iris recognition ultimately depends on your organization’s specific requirements, environment, and security goals. Both biometric technologies offer unique strengths, and understanding their ideal applications is key to making the right decision.
If your top priority is security, such as in border control, military facilities, prison systems, or national ID programs, reconnaissance de l'iris is often the preferred solution. Its extremely low false acceptance rate and resistance to spoofing make it ideal for high-security biometric authentication. Government institutions and large-scale identification programs benefit greatly from the unmatched precision and long-term reliability of iris scanning. Even in harsh environmental conditions or low light, iris recognition maintains consistent accuracy.
If convenience, speed, and user experience are more important, la reconnaissance faciale is the better option. It is widely used in smart access control systems, employee attendance tracking, retail checkout terminals, and transportation hubs. Facial recognition is fast, non-intrusive, and suitable for high-traffic areas where quick identity verification is essential. It supports hands-free access, improving hygiene and efficiency in modern workplaces or public spaces.
In some cases, combining both facial and iris recognition in a multi-modal biometric system can offer the best of both worlds. This layered approach enhances both security and flexibility. For example, banks, airports, or corporate campuses can implement dual biometric authentication to allow both rapid entry and high-assurance identity verification when needed. Multi-modal systems also help reduce failure rates and accommodate more diverse user populations.
Whether you choose facial recognition or iris recognition, the decision should be based on a clear understanding of the technology’s capabilities and your operational goals. Consider factors like user volume, environment, required level of security, cost, and integration needs when selecting a biometric solution.
Key Applications of Facial and Iris Recognition
Facial Recognition Applications
Smart access control systems
Airport and border security
Retail and payment terminals
Time attendance and visitor management
Mobile device unlocking
Facial Recognition Application Video
Iris Recognition Applications
Government ID and e-passports
Prison and military facility access
High-security financial transactions
Healthcare identity verification
Iris recognition application video
Conclusion
Both technologies have their strengths. If your goal is speed and convenience, go with facial recognition. If precision and security are more critical, choose iris recognition. In today’s landscape, some advanced systems even combine both, ensuring the highest standard of security.
Ultimately, the choice between facial recognition or iris recognition depends on your organization’s needs, user environment, and security level required.
FAQ
Iris recognition is generally more secure due to the complexity of the iris pattern and resistance to spoofing. However, facial recognition systems with liveness detection also offer robust security.
Some facial recognition systems use infrared to work in low-light environments, but performance can vary. Iris recognition is more consistent in such conditions.
Facial recognition is typically faster, as it requires less user interaction. Iris recognition, while more accurate, may require the user to be at a specific distance and angle.
Yes, iris recognition devices generally cost more due to specialized infrared cameras and software requirements.
Absolutely. Many modern security systems offer multi-modal biometric authentication, combining facial, iris, fingerprint, and even palm vein recognition for maximum flexibility and security.