Biometric healthcare refers to the use of unique physiological or behavioral characteristics of the human body, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scans, and voice patterns, to identify and authenticate individuals.
In the healthcare sector, this technology is increasingly being integrated to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the patient identification process. By using biometrics, healthcare providers can ensure that they are accessing the correct patient records, thereby reducing the risk of medical errors and improving overall patient safety.
This innovative approach not only simplifies administrative tasks, but also protects sensitive health information, providing a more secure and personalized healthcare experience.
Here are some common biometric technologies:
Fingerprint recognition: This method involves capturing an image of a person’s fingertips. It is widely used due to its reliability and ease of use.
Бет-әлпетті тану:
This technology analyzes features of a person’s face, including the distance between the eyes, the shape of the chin, and the outline of the lips. It is often used in identification systems.
Iris scanning:
Iris recognition uses unique patterns in the colored rings of the eyeballs. It is considered very accurate and is often used in high-security environments. For example, operating rooms
Дауысты тану:
This technology identifies individuals based on unique features of their voice, such as pitch, tone, and rhythm. It is often used in telecommunications and call centers.
Palm print recognition:
This involves measuring and analyzing the shape and size of a person’s hand, including the length and width of the fingers. This method is less common but is used in some access control systems.
Each biometric method has its own advantages and challenges, and its suitability varies depending on the environment and security requirements.
HFSECURITY Biometric Healthcare Solution
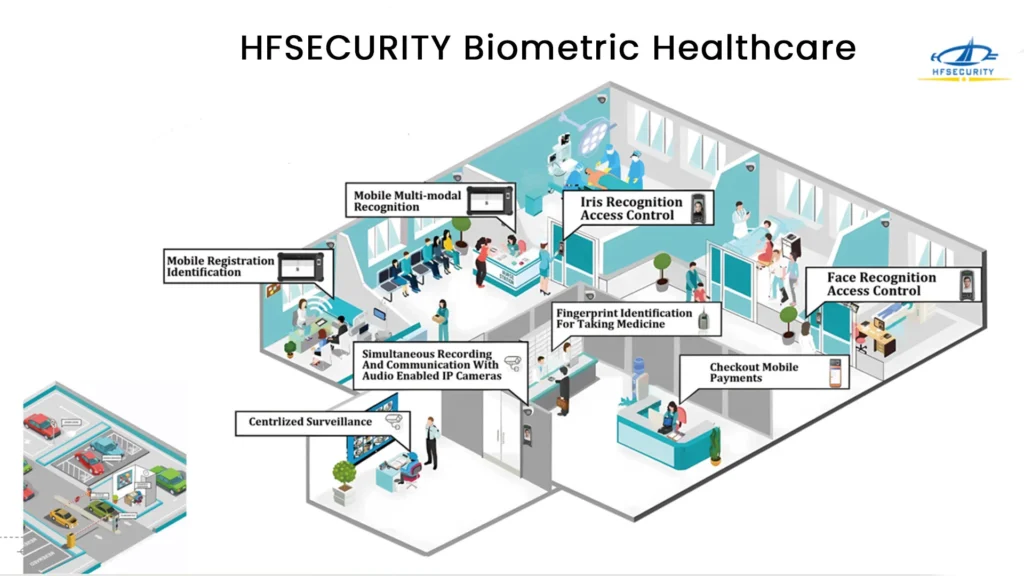
This image shows a HFSECURITY comprehensive hospital solution, which focuses on using high-tech biometric feature technology and monitoring systems to improve hospital operational efficiency and patient safety. Specific contents include:
- Mobile Registration: Patients can pre-register through mobile devices, reducing on-site queuing time and improving reception efficiency.
- Iris Recognition Access Control: Control personnel access to sensitive areas through iris recognition technology to ensure regional security.
- Face Recognition: Facial recognition technology is used to identify people entering the hospital and enhance security monitoring.
- Fingerprint Identification and Communication Recording: Use fingerprint recognition technology for identity authentication and record communication activities to facilitate tracking and recording of communication information.
- Mobile Payments: Patients can pay medical expenses through mobile phone applications, which is convenient and fast.
- Centralized Surveillance: The centralized monitoring system monitors various areas of the hospital to ensure the overall safety of the hospital.
The purpose of the entire solution is to improve the safety standards and work efficiency of the hospital by integrating different technologies, while also providing patients with a more convenient and safe service experience. This type of solution is particularly suitable for large hospitals, where it can effectively manage large flows of patients and visitors and ensure the quality and safety of medical services.
Biometric Healthcare Application
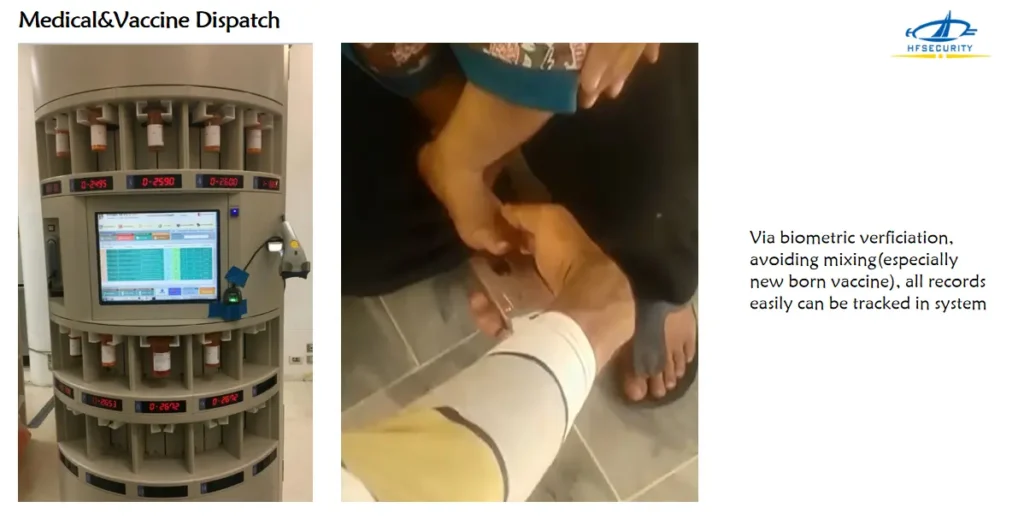
Biometric Healthcare in medical &vaccine dispatch
Via biometric verification, avoding mixing(especially new born vaccine)all records easily can be tracked in systems
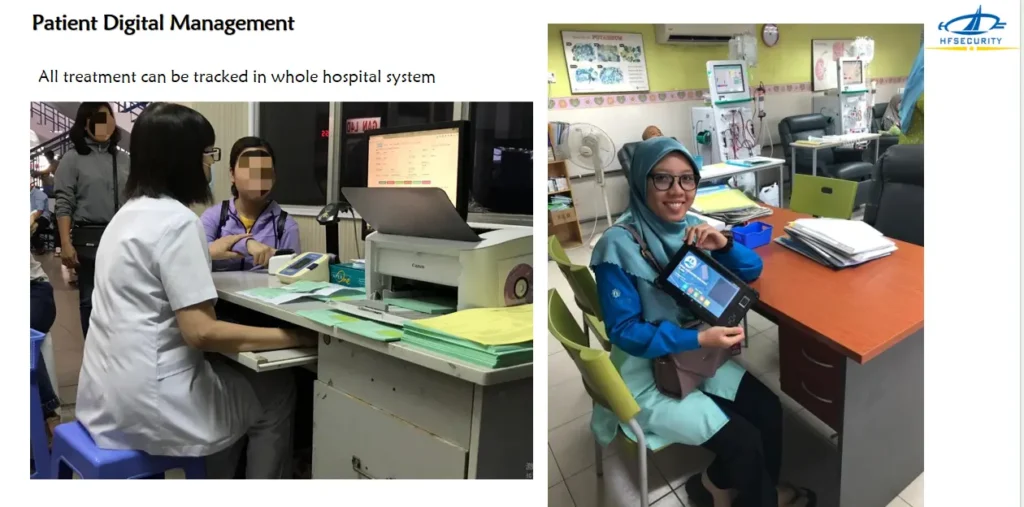

Biometric Healthcare in Patient Digital Management
All treatment can be tracked in whole hospital system
Biometric Healthcare Advantages
Biometric technology plays a vital role in enhancing patient identification and data management in healthcare systems. Its contributions to these areas are as follows
Patient Identification
Дәлдік пен сенімділік:
Biometric systems use unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, or voice recognition, to accurately identify patients. This minimizes errors associated with misidentification of patients, which can lead to inappropriate treatment or medication errors.
Тиімділігі:
By streamlining the identification process, biometrics reduce the time required to verify a patient’s identity during an admission, outpatient, or emergency visit. This increases workflow efficiency and improves the patient experience.
Reduce Duplicate Records:
Biometric systems help eliminate duplicate medical records, ensuring that each patient is registered in a unique manner. This prevents patient data from being fragmented across different systems or departments.
Алаяқтықтың алдын алу:
By using biometric identifiers, healthcare systems can prevent identity theft and insurance fraud, ensuring legitimate individuals have access to services and benefits.
Data Management
Secure Access to Information:
Biometrics provide a powerful way to authenticate healthcare providers and staff who access sensitive patient data. This enhances data security by ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to electronic health records (EHRs) and other confidential information.
Аудит және есеп берушілік:
Biometric systems can be integrated into data management processes to create a detailed audit trail. This helps track who accessed patient data and when, ensuring accountability and regulatory compliance.
Interoperability and Integration:
Biometric systems can be integrated with other health information systems, facilitating seamless data exchange and interoperability between different platforms and institutions.
Patient Consent and Data Sharing:
Biometrics can be used to manage patient consent for data sharing. Patients can verify their identity through biometrics to approve or deny access to their health information, giving them greater control over their personal data.
Biometrics can significantly enhance patient care and improve the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery in a number of ways.
Biometric Healthcare use in Improving Patient Care:
Personalized Medicine
Customized Treatment:
Biometric data, such as genetic and physiological information, can help healthcare providers develop personalized treatment plans that are more effective for individual patients. This approach can lead to better outcomes by taking into account each patient’s unique characteristics.
Improving Patient Safety
Accurate Patient Identification:
Biometric technology ensures that patients are correctly identified, reducing the risk of medical errors, such as giving a patient the wrong medication or treatment. This accuracy is critical, especially in emergency situations or when dealing with patients who are unable to communicate.
Medication Management:
Biometric systems can verify the identity of the patient before dispensing medication and can also verify the identity of the physician, ensuring accurate and secure prescriptions.
Streamline clinical workflows
Efficient admissions and discharges:
By using biometrics, healthcare organizations can expedite the admission and discharge process, reduce wait times, and improve the overall patient experience.
Quick access to medical records:
Biometrics enable healthcare professionals to quickly and securely access patient records to make timely and informed decisions.
Enhanced monitoring and diagnosis
Remote monitoring:
Wearable biometric devices can continuously monitor a patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels. This data can be transmitted to healthcare providers in real time, allowing for proactive management of chronic conditions and early intervention when necessary.
Accurate diagnosis:
Biometrics can help with more precise diagnoses by providing detailed physiological data that can be used to accurately assess health status.
Increase patient engagement
Patient portals and apps:
Biometrics can be used to securely verify patient identity when patients access personal health information through portals and apps. This enables patients to actively participate in their own care, leading to better health management and adherence to treatment plans.
Support for Telemedicine
Secure Virtual Consultations:
Biometrics can enhance the security of telemedicine platforms by ensuring both patients and healthcare providers are authenticated prior to a virtual consultation, preserving the confidentiality and integrity of medical interactions.
Real-world applications and case studies of biometrics in healthcare have shown how effective it is in enhancing patient care, improving safety, and streamlining operations. Here are some examples:
Biometric in Healthcare Application
- Науқасты дәл анықтау
Case Study: Hospital in New YorkA hospital in New York implemented a palm vein scanning system to improve the accuracy of patient identification. This biometric approach significantly reduced instances of misidentification of patients, which reduced medical errors and improved patient safety. - Secure Access to Medical Records
Application: Biometric Authentication in EHR SystemsSeveral healthcare organizations have integrated biometric authentication into their electronic health record (EHR) systems. For example, a large hospital network in the Midwest uses fingerprint scanning to securely access patient records, ensuring that only authorized healthcare professionals can view sensitive information. This reduces incidents of unauthorized access. - Medication Administration Security
Case Study: Pediatric Hospital in CaliforniaA pediatric hospital implemented fingerprint scanning to verify patient identity before administering medication. The system ensures that young patients receive the correct medication and dosage, significantly reducing medication errors and improving patient safety. - Continuous Health Monitoring
Application: Wearable Biometric Devices Some healthcare providers use wearable biometric devices to monitor patients with chronic conditions such as heart disease or diabetes. These devices track vital signs and transmit data to the medical team in real time, allowing for early detection of potential health issues and timely intervention. Patients report that their condition management has improved as a result. - Infection Control
Case Study: Contactless Biometric Systems in Singapore Hospitals In response to the COVID-19 outbreak, hospitals in Singapore have adopted contactless biometric systems such as facial recognition for patient registration and staff access control. This reduces physical touchpoints and helps manage infection risks within healthcare facilities. - Emergency Situations
Application: Rapid Identification in Emergency Rooms Some emergency departments have implemented iris scanning to quickly identify unconscious or unresponsive patients. This enables healthcare providers to access critical medical history and make informed decisions quickly, improving the chances of successful intervention in emergency situations.



