Using biometric fingerprint scanner for attendance involves using an individual’s unique fingerprint as a means of identification and authentication when recording their attendance. Instead of relying on traditional methods like manual sign-in sheets or swipe cards, biometric fingerprint scanners provide a more secure, accurate, and efficient way to manage attendance records.
Advantages of using biometric fingerprint scanner for attendance
Here are some advantages of using biometric fingerprint scanner for attendance over traditional methods:
- Enhanced Security: Fingerprint scanners offer a high level of security since fingerprints are unique to each individual. It is extremely difficult to forge or duplicate someone’s fingerprint, making it a reliable method for verifying identity and preventing fraudulent activities like buddy punching (when employees clock in or out for each other).
- Accurate and Reliable: Fingerprint recognition technology has advanced significantly, resulting in high accuracy rates. Biometric systems can reliably identify individuals based on their unique fingerprint patterns, eliminating errors associated with manual data entry or misplaced swipe cards. This ensures accurate attendance tracking and eliminates discrepancies in payroll calculations.
- Speed and Efficiency: Fingerprint scanning is a quick and efficient process. Employees can authenticate their attendance by simply placing their finger on the scanner, and the system instantly verifies their identity and records the timestamp. This eliminates the need for employees to carry and swipe cards or sign-in manually, saving time for both employees and administrators.
- Elimination of Proxy Attendance: Proxy attendance, where one employee records attendance on behalf of another, can be completely eliminated with biometric fingerprint scanners. Since fingerprints are unique to individuals, it becomes nearly impossible for someone to clock in or out on behalf of another person, ensuring greater accountability and fairness in attendance tracking.
- Streamlined Data Management: Biometric attendance systems often come with integrated software that automates the data management process. Attendance records are securely stored and easily accessible, reducing administrative work and enabling efficient tracking and reporting. This data can also be integrated with payroll systems, simplifying salary calculations and reducing errors.
- Cost-Effective: While the initial investment in biometric fingerprint scanners may be higher than traditional attendance systems, they offer long-term cost savings. The elimination of costs associated with swipe cards or ID badges, reduced administrative work, and prevention of time theft or buddy punching all contribute to cost savings for organizations.
- Hygienic and Contactless: In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, contactless solutions have become increasingly important. Biometric fingerprint scanners offer a hygienic solution as they require minimal physical contact and do not involve shared surfaces like swipe cards or touch screens, reducing the risk of spreading germs.
In summary, using biometric fingerprint scanner for attendance offers enhanced security, accuracy, efficiency, and cost savings compared to traditional methods. These systems provide a reliable and convenient way to manage attendance records while ensuring the integrity of data and promoting a fair and accountable work environment.
Biometric fingerprint scanner work by capturing and analyzing the unique patterns and characteristics present in an individual’s fingerprint. Here’s an overview of the technology behind biometric fingerprint scanners:

Process of Biometric Fingerprint Scanner for attendance
- Image Capture: The first step in the process involves capturing an image of the fingerprint. The scanner uses various technologies, such as optical, capacitive, or ultrasonic, to capture a high-resolution image of the ridges and valleys on the fingertip.
- Minutiae Extraction: Once the image is captured, the scanner analyzes it to identify and extract specific features called minutiae points. Minutiae points are specific points where ridges end, bifurcate, or intersect. Examples include ridge endings, ridge bifurcations, and enclosures.
- Template Creation: The extracted minutiae points are used to create a mathematical representation of the fingerprint called a fingerprint template. This template is a unique and compact representation of the fingerprint that can be stored and compared for future identification purposes.
- Enrollment: During the enrollment process, an individual’s fingerprint is scanned multiple times to capture a set of reference templates. These reference templates are stored in a database for future matching and identification.
- Matching and Verification: When an individual presents their fingerprint for attendance verification, the scanner captures a new image and extracts the minutiae points. The system then compares the extracted minutiae points with the reference templates stored in the database to find a match. If the extracted minutiae points align with a stored template within a certain threshold, the system verifies the person’s identity.
- False Rejection and False Acceptance: Biometric fingerprint scanner have a threshold for matching that determines whether a fingerprint is accepted or rejected. False rejection occurs when a legitimate fingerprint is not recognized, while false acceptance happens when an unauthorized fingerprint is incorrectly recognized as a match. These rates can be adjusted to balance security and convenience based on the system’s requirements.
- Liveness Detection: To prevent spoofing or the use of artificial replicas, modern fingerprint scanners incorporate liveness detection mechanisms. These mechanisms check for the presence of vital signs in the fingerprint, such as blood flow or sweat, to ensure that the presented fingerprint is from a live person and not a fake or copied fingerprint.
- Security and Encryption: To protect the stored fingerprint templates and ensure data privacy, biometric fingerprint scanners often employ encryption techniques. These techniques ensure that the templates are securely stored and cannot be easily reverse-engineered or accessed by unauthorized individuals.
It’s important to note that different types of fingerprint scanners may employ varying technologies and algorithms. Optical scanners use light and sensors to capture fingerprint images, while capacitive scanners utilize an array of tiny capacitors to detect ridges and valleys. Ultrasonic scanners, on the other hand, emit ultrasonic waves to create a detailed 3D image of the fingerprint. The choice of technology depends on factors like accuracy, cost, and the specific requirements of the application.
Overall, biometric fingerprint scanners rely on advanced image processing, pattern recognition, and encryption techniques to accurately capture, analyze, and match fingerprint data for identification and verification purposes.
Choosing the Right Biometric Fingerprint Scanner for attendance
When choosing the right biometric fingerprint scanner for attendance, several factors should be considered to ensure it meets the specific needs of your organization. Here are some key points to consider:
- Accuracy: Accuracy is a crucial factor when selecting a fingerprint scanner. Look for scanners that have a high accuracy rate in capturing and matching fingerprints. It’s essential to choose a scanner that minimizes false rejections (legitimate fingerprints not recognized) and false acceptances (unauthorized fingerprints recognized as a match).
- Technology: Consider the technology used in the fingerprint scanner. Optical, capacitive, ultrasonic, and thermal scanners have different capabilities and performance characteristics. Assess the advantages and limitations of each technology based on factors like image quality, resistance to contaminants, and anti-spoofing measures.
- Speed and Efficiency: Evaluate the speed and efficiency of the fingerprint scanner. A fast scanner ensures quick authentication and reduces wait times for employees. Look for scanners that provide rapid image capture and matching without compromising accuracy.
- Robustness and Durability: Consider the durability of the fingerprint scanner, especially if it will be used in demanding environments or high-traffic areas. The scanner should be resistant to wear and tear, moisture, and dirt. Look for scanners with a solid build quality and suitable IP (Ingress Protection) ratings for the intended environment.
- Integration and Compatibility: Check the compatibility of the fingerprint scanner with the attendance management system or software you plan to use. Ensure that the scanner can seamlessly integrate with the existing infrastructure and the software can support the scanner’s data format and protocols.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the fingerprint scanner system. If your organization is expected to grow or if you have multiple locations, choose a scanner that can be easily scaled up to accommodate a larger number of users and can be integrated with a centralized attendance management system.
- User Experience: Evaluate the user experience of the fingerprint scanner. It should be user-friendly, intuitive, and easy to operate for employees. Consider factors such as ease of finger placement, clear instructions, and visual feedback.
- Cost: Determine the budget allocated for the fingerprint scanner system. Consider the initial investment, maintenance costs, and any additional software or licensing fees. Balance the cost with the required features and the long-term benefits the system will provide.Biometric fingerprint scanner for sale also need to think
- Support and Warranty: Assess the level of support provided by the scanner manufacturer or vendor. Look for warranties, technical support, and software updates to ensure long-term usability and troubleshooting assistance.
- Security and Compliance: Ensure that the fingerprint scanner system meets security standards and regulatory requirements. Look for scanners that employ encryption techniques to protect stored data and have features like liveness detection to prevent spoofing attempt
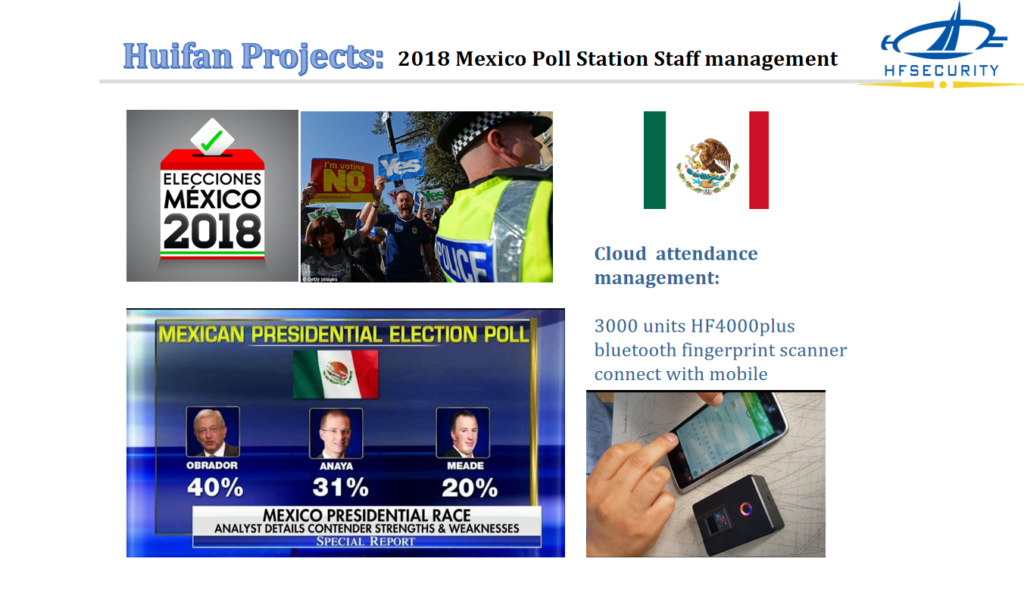
Ten steps of use biometric fingerprint scanner for attendance
- Assess your requirements: Determine the number of employees/students, the desired level of security, and the specific features you need in a fingerprint scanner system. This will help you choose the right hardware and software solution.
- Purchase the hardware: Research and purchase a biometric fingerprint scanner that suits your needs. Consider factors such as accuracy, capacity, connectivity options, and durability. You may also need additional equipment like access control panels or time attendance software.
- Install the hardware: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to physically install the fingerprint scanner. Typically, this involves mounting the scanner on a suitable surface or integrating it with an access control panel.
- Connect the scanner: Connect the fingerprint scanner to your computer network or the central attendance management system. This usually involves plugging in the scanner to a USB port or connecting it via Ethernet or Wi-Fi, depending on the scanner’s capabilities.
- Install the software: Install the necessary software for the fingerprint scanner system. This could be a dedicated attendance management software or an SDK (Software Development Kit) provided by the scanner manufacturer.
- Configure the software: Once the software is installed, configure it according to your requirements. Set up user profiles for each employee/student, define attendance rules, and customize settings such as attendance reports, shift schedules, and overtime calculations.
- Enroll employees/students: Begin enrolling the fingerprints of individuals who will be using the system. Each person’s fingerprint needs to be captured and stored in the system’s database. This is typically done by having individuals place their fingers on the scanner multiple times to capture a reliable fingerprint template.
- Test the system: Perform thorough testing to ensure the system is functioning correctly. Verify that individuals can successfully authenticate their fingerprints, and attendance data is accurately recorded and processed.
- Train users: Provide training to employees/students on how to use the fingerprint scanner system. Familiarize them with the enrollment process, fingerprint placement techniques, and any additional features or functionalities.
- Deploy and monitor: Once the system is fully configured and tested, deploy it for regular use. Monitor the system’s performance, troubleshoot any issues that arise, and periodically maintain and update the software and hardware as required.
It’s important to note that the specific steps may vary depending on the brand and model of the fingerprint scanner system you choose, as well as any additional features or integrations you require. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation and guidelines for detailed instructions tailored to your specific system.
what is Enrollment Process for fingerprint scanner time attendance
The enrollment process for a fingerprint scanner time attendance system involves capturing and storing the fingerprints of individuals who will be using the system. Here’s a general overview of the enrollment process:
- Prepare the system: Ensure that the fingerprint scanner and attendance management software are properly installed and configured.
- Gather user information: Collect the necessary information about each individual, such as their name, employee/student ID, and any other relevant details required for attendance management.
- Start enrollment mode: Activate the enrollment mode on the fingerprint scanner or within the attendance management software. This mode allows you to capture and store fingerprint templates.
- Capture fingerprints: Instruct the individual to place their finger on the scanner’s fingerprint sensing area. The scanner will capture multiple images of the fingerprint, usually by taking several scans of the finger.
- Quality check: The system will assess the quality of the captured fingerprint images to ensure they are clear and of sufficient quality for accurate recognition. If the images are not satisfactory, you may need to ask the individual to place their finger on the scanner again.
- Create a fingerprint template: Using the captured fingerprint images, the system generates a unique fingerprint template for that individual. The template is a mathematical representation of the fingerprint that the system uses for subsequent matching and authentication.
- Store the fingerprint template: The generated fingerprint template is securely stored in the system’s database or on a centralized server. This template will be used for future comparisons when the individual verifies their attendance using their fingerprint.
- Repeat for each individual: Repeat the above steps for each employee or student who needs to be enrolled in the system. Ensure that all necessary information is accurately recorded and linked to the corresponding fingerprint template.
- Verify enrollment: After enrolling individuals, perform a verification process to ensure that the captured fingerprint templates can be successfully matched and authenticated by the system. This helps confirm that the enrollment process was successful and the system is ready for use.
The specific steps and interface for enrollment may vary depending on the fingerprint scanner and attendance management software you are using. It is essential to consult the user manual or documentation provided by the manufacturer for detailed instructions on the enrollment process for your specific system.
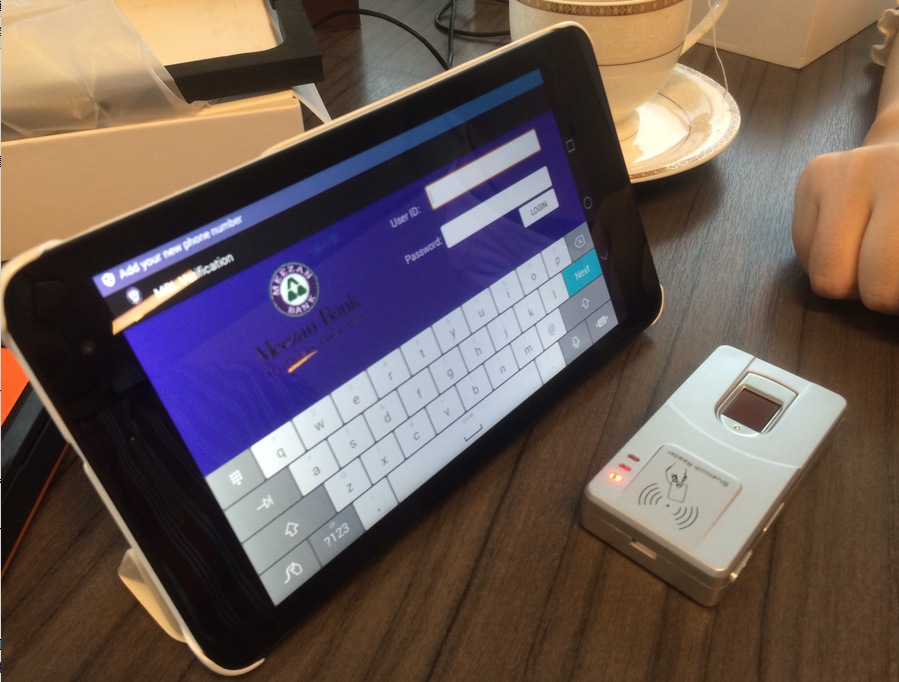
Discuss the integration of the fingerprint scanner with attendance management software to automate the attendance tracking process.
Integrating a fingerprint scanner with attendance management software allows for the automation of the attendance tracking process. This integration enables a seamless and efficient way to record attendance data and eliminates the need for manual entry or traditional timekeeping methods. Here are the key aspects of integrating a fingerprint scanner with attendance management software:
- Biometric data capture: The fingerprint scanner captures unique biometric data, such as fingerprints, of individuals during the enrollment process. This data is converted into a digital template that represents the unique features of each person’s fingerprint.
- Data synchronization: The fingerprint scanner is connected to the attendance management software, either directly or through a network. This allows for real-time synchronization of data between the scanner and the software. Attendance management software often provides specific modules or APIs to facilitate this integration.
- Attendance tracking: When an individual needs to mark their attendance, they place their finger on the scanner, which captures their fingerprint. The fingerprint is then compared with the stored templates in the attendance management software’s database to verify the individual’s identity.
- Real-time attendance records: Upon successful verification, the attendance management software records the attendance data, including the date, time, and identity of the individual. This information is stored in the software’s database, enabling real-time tracking of attendance.
- Automated calculations: The attendance management software can automatically calculate working hours, overtime, and other attendance-related metrics based on the recorded data. This streamlines payroll processing, leave management, and other attendance-related tasks.
- Reporting and analytics: The integrated system can generate comprehensive attendance reports and analytics, providing insights into attendance patterns, late arrivals, absenteeism rates, and more. These reports help managers and administrators make informed decisions and identify trends or issues.
- Integration with other systems: The attendance management software can be further integrated with other systems, such as payroll software or HR management systems. This allows for seamless data flow between different departments and processes, reducing manual efforts and ensuring data accuracy.
- Security and data privacy: Biometric data is sensitive, and it is crucial to prioritize security and data privacy when integrating a fingerprint scanner with attendance management software. Implementing encryption, access controls, and other security measures ensures the protection of biometric data and attendance records.
By integrating a fingerprint scanner with attendance management software, organizations can streamline the attendance tracking process, eliminate manual errors, improve accuracy, and enhance overall efficiency. It simplifies administrative tasks, saves time, and provides valuable insights for effective workforce management.
When troubleshooting common issues with a fingerprint scanner time attendance system, here are some steps you can take:
- Clean the fingerprint scanner: Over time, the scanner may accumulate dirt, oil, or residue, which can affect its accuracy. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to clean the scanner’s surface gently. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage the scanner.
- Check the power and connections: Ensure that the fingerprint scanner is receiving power and that all the cables and connections are properly connected. Sometimes, a loose connection can cause issues with the device.
- Verify the fingerprint database: Make sure that the fingerprint database is accurate and up to date. Check if the fingerprints of the users are properly enrolled in the system. If any fingerprint data is corrupted or missing, re-enroll the affected individuals’ fingerprints.
- Adjust the scanner settings: Check the settings of the fingerprint scanner to ensure they are configured correctly. Some scanners allow you to adjust the sensitivity or threshold for accepting fingerprints. Experiment with different settings to see if it improves the accuracy or recognition rate.
- Update the firmware or software: Check if there are any available firmware or software updates for the fingerprint scanner. Manufacturers often release updates to address bugs or improve performance. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to install the latest updates.
- Troubleshoot software conflicts: If the fingerprint scanner is connected to a computer or a network, ensure that there are no software conflicts or compatibility issues. Check if the required drivers or software are installed correctly. If necessary, uninstall and reinstall the drivers or software.
- Test with different fingers or individuals: Sometimes, certain individuals may have difficulty with fingerprint recognition due to factors like dry skin, injuries, or aging. Test the scanner with different fingers or individuals to see if the issue persists. If the scanner consistently fails to recognize a specific finger, that finger may need to be re-enrolled or replaced with another finger.
- Consult the manufacturer or technical support: If you’ve tried the above steps and are still experiencing issues, reach out to the manufacturer’s technical support or customer service. They can provide specific guidance based on the model of the fingerprint scanner and help troubleshoot any complex problems.
Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines while troubleshooting the fingerprint scanner time attendance system.
Example of organization use biometric fingerprint scanner for attendance
Here are a few real-life examples of organizations that have successfully implemented biometric fingerprint scanners for attendance management:
- Walmart: Walmart, one of the largest retail companies in the world, implemented biometric fingerprint scanners across its stores to manage employee attendance. The system helped automate the process, eliminate manual errors, and reduce time theft. By accurately tracking employee attendance, Walmart was able to improve workforce management and streamline payroll processes.
- Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS): RBS, a leading banking institution, implemented biometric fingerprint scanners to enhance security and streamline employee attendance. The scanners were integrated with the bank’s time and attendance system, allowing employees to clock in and out using their fingerprints. The biometric system not only improved accuracy but also reduced the risk of buddy punching (when one employee clocks in on behalf of another), enhancing overall payroll accuracy and security.
- Dubai Police: The Dubai Police force implemented biometric fingerprint scanners for their personnel to accurately record attendance and ensure the presence of officers at designated locations. The system helped prevent time fraud and improved accountability among officers. It also provided an efficient way to track shifts and manage workforce scheduling.
- Manchester Airport: Manchester Airport in the UK adopted biometric fingerprint scanners to manage staff attendance and access control. The system enabled seamless integration with their existing workforce management system and allowed employees to quickly clock in and out using their fingerprints. The biometric solution increased accuracy, reduced administrative burdens, and enhanced security by eliminating the need for traditional access cards.
- Toyota Kirloskar Motor: Toyota Kirloskar Motor, a subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation in India, implemented biometric fingerprint scanners for attendance management in their manufacturing facilities. The scanners streamlined the attendance process and improved accuracy by eliminating the need for manual timekeeping. The system also provided real-time visibility into workforce attendance patterns and helped identify areas for process improvement.

These examples highlight the benefits of implementing biometric fingerprint scanners for attendance management, including increased accuracy, enhanced security, streamlined processes, and improved workforce management. However, it is important to note that the success of such implementations depends on various factors, including proper planning, system integration, and user adoption.
Emerging trends and advancements in biometric technology are poised to have a significant impact on attendance management systems in the future. Here are some key trends to consider:
- Multimodal Biometrics: Rather than relying solely on fingerprint scanning, attendance management systems are increasingly adopting multimodal biometrics. This involves combining multiple biometric modalities such as fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scans, voice recognition, or even behavioral biometrics like gait recognition. Multimodal systems offer increased accuracy, security, and flexibility, as they can adapt to different environmental conditions and accommodate individuals with physical limitations.
- Contactless Biometrics: With the growing need for hygienic and touchless solutions, contactless biometric technologies are gaining traction. Attendance management systems are incorporating contactless modalities like facial recognition or palm vein recognition, reducing the need for physical contact with the scanner. These solutions not only improve hygiene but also offer convenience and speed in high-traffic environments.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are being applied to biometric systems to enhance accuracy, speed, and robustness. These technologies can analyze large datasets, learn from patterns, and adapt to variations in biometric traits. By leveraging AI and ML, attendance management systems can improve identification and verification accuracy, reduce false positives and negatives, and handle complex scenarios more effectively.
- Cloud-Based Biometric Systems: Cloud computing is enabling the deployment of biometric systems in a scalable and cost-effective manner. Cloud-based attendance management systems offer centralized data storage, seamless integration with other systems, and real-time access from any location. This enables organizations with multiple branches or remote workforces to efficiently manage attendance across different locations.
- Wearable Biometrics: Wearable devices equipped with biometric sensors present new opportunities for attendance management. Smartwatches or wristbands with biometric capabilities can track individuals’ unique physiological traits, such as heart rate or electrocardiogram (ECG), to verify their identity for attendance purposes. Wearable biometrics offer convenience, portability, and the potential for continuous authentication.
- Biometric Data Privacy and Regulations: As biometric technologies advance, data privacy and regulations become even more critical. Emerging trends include the development of privacy-enhancing techniques, such as secure enclaves and encrypted biometric templates, to protect sensitive data. Additionally, regulations and standards around biometric data collection, storage, and usage, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), are evolving to ensure individuals’ rights and consent are respected.
- Integration with Internet of Things (IoT): Attendance management systems can integrate with IoT devices to provide seamless and automated attendance tracking. For example, smart door locks or access control systems can be connected to biometric scanners, enabling employees to gain access to a facility based on their biometric authentication, automatically recording their attendance in the process.
These emerging trends and advancements in biometric technology hold great promise for the future of attendance management systems. By leveraging these innovations, organizations can achieve higher accuracy, improved security, enhanced user experience, and increased efficiency in managing employee attendance.
HFSECURITY Biometric Fingerprint Scanner for attendance
HFSECURITY is a company that specializes in the production and development of fingerprint scanners for time attendance systems. They offer a range of biometric fingerprint scanners designed to accurately record employee attendance, enhance security, and streamline workforce management processes. HFSECURITY focuses on providing reliable and user-friendly solutions for businesses across various industries.
Some key features and offerings of HFSECURITY fingerprint scanners for time attendance include:
- High Accuracy:
HFSECURITY fingerprint scanners utilize advanced fingerprint recognition algorithms to ensure accurate and reliable identification of individuals. This helps eliminate errors and prevent instances of time theft or buddy punching.
- Fast Identification Speed:
The scanners are designed for efficient performance, offering quick identification and verification of employees’ fingerprints. This ensures a smooth and streamlined attendance management process.
- Robust Security:
HFSECURITY prioritizes data security and implements encryption protocols to protect the biometric data captured by their scanners. This helps safeguard sensitive information and ensures compliance with privacy regulations.
- Interface conviviale :
The fingerprint scanners feature user-friendly interfaces that make it easy for employees to enroll their fingerprints and clock in or out. Intuitive interfaces contribute to a positive user experience and facilitate widespread adoption within organizations.
- Integration Capabilities:
HFSECURITY fingerprint scanners are compatible with various attendance management software systems, enabling seamless integration into existing infrastructure. This allows for centralized attendance data management and simplified reporting and analysis.
- Durability and Reliability:
HFSECURITY focuses on producing high-quality fingerprint scanners that are durable and reliable, making them suitable for demanding environments such as factories, offices, or construction sites.
It is worth noting that while HFSECURITY is a specific company that provides fingerprint scanners for time attendance, there are also several other reputable companies in the market offering similar products. When selecting a fingerprint scanner for time attendance, it is essential to assess your specific requirements, consider factors such as system compatibility, customer support, and overall product reputation, and choose a solution that best fits your organization’s needs.



