Giải pháp sinh trắc học dành cho ngân hàng xác minh danh tính của cá nhân. Những đặc điểm này có thể bao gồm dấu vân tay, mẫu mống mắt, đặc điểm khuôn mặt, giọng nói hoặc thậm chí là các đặc điểm hành vi như mẫu đánh máy hoặc nhận dạng dáng đi. Sự liên quan của nhận dạng sinh trắc học trong các dịch vụ tài chính là rất quan trọng và tiếp tục tăng lên do một số lý do:
- Bảo mật nâng cao: Mã định danh sinh trắc học cung cấp mức độ bảo mật cao so với các phương pháp xác thực truyền thống như mật khẩu hoặc mã PIN, vốn có thể bị đánh cắp hoặc dễ đoán. Các đặc điểm sinh trắc học là duy nhất đối với mỗi cá nhân, khiến việc mạo danh người khác trở nên cực kỳ khó khăn.
- Trải nghiệm người dùng thuận tiện và liền mạch: Xác thực sinh trắc học mang lại trải nghiệm thân thiện và thuận tiện hơn. Người dùng có thể dễ dàng truy cập tài khoản tài chính hoặc thực hiện giao dịch chỉ bằng cách sử dụng các đặc điểm sinh trắc học của họ, loại bỏ nhu cầu phải nhớ mật khẩu phức tạp hoặc mang theo mã thông báo vật lý.
- Phòng chống gian lận: Nhận dạng sinh trắc học có thể làm giảm đáng kể gian lận trong các dịch vụ tài chính. Các đặc điểm sinh trắc học rất khó làm giả hoặc sao chép, khiến tội phạm khó có thể mạo danh người khác và truy cập trái phép vào tài khoản hoặc thực hiện các giao dịch gian lận.
- Tuân thủ hợp lý: Các tổ chức tài chính phải tuân thủ nhiều yêu cầu pháp lý và tiêu chuẩn tuân thủ khác nhau để ngăn chặn rửa tiền, gian lận và trộm cắp danh tính. Nhận dạng sinh trắc học có thể giúp đáp ứng các nghĩa vụ tuân thủ này bằng cách đảm bảo tính xác thực của danh tính khách hàng và cho phép xác thực khách hàng mạnh mẽ.
- Xác thực từ xa: Với sự gia tăng của ngân hàng kỹ thuật số và dịch vụ tài chính từ xa, nhận dạng sinh trắc học cung cấp một cách an toàn để xác thực khách hàng từ xa. Nó cho phép các tổ chức tài chính cung cấp các dịch vụ như mở tài khoản trực tuyến, đơn xin vay hoặc ngân hàng di động một cách an toàn và hiệu quả.
- Cải thiện trải nghiệm của khách hàng: Xác thực sinh trắc học có thể nâng cao trải nghiệm chung của khách hàng bằng cách giảm ma sát trong các giao dịch tài chính. Nó loại bỏ nhu cầu về các quy trình xác thực dài dòng và cho phép truy cập nhanh chóng và an toàn vào các dịch vụ tài chính, tăng sự hài lòng của khách hàng.
- Khả năng mở rộng và hiệu quả về chi phí: Khi công nghệ sinh trắc học phát triển, chúng trở nên hợp lý hơn và có khả năng mở rộng hơn. Các tổ chức tài chính có thể triển khai hệ thống nhận dạng sinh trắc học trên nhiều kênh, chẳng hạn như ATM, ứng dụng di động hoặc trung tâm dịch vụ khách hàng, đảm bảo trải nghiệm người dùng nhất quán và an toàn.
Tuy nhiên, điều quan trọng cần lưu ý là việc áp dụng nhận dạng sinh trắc học trong các dịch vụ tài chính cũng làm dấy lên mối lo ngại về quyền riêng tư, bảo mật dữ liệu và khả năng sử dụng sai dữ liệu sinh trắc học. Các biện pháp bảo vệ thích hợp và tuân thủ các quy định bảo vệ dữ liệu hiện hành là rất quan trọng để giải quyết những mối lo ngại này và đảm bảo việc sử dụng công nghệ sinh trắc học một cách có trách nhiệm.
Tầm quan trọng của việc xác minh danh tính chặt chẽ trong lĩnh vực tài chính.
Xác minh danh tính chặt chẽ có tầm quan trọng tối cao trong lĩnh vực tài chính vì một số lý do:
- Ngăn ngừa gian lận và tội phạm tài chính: Xác minh danh tính đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc ngăn ngừa gian lận, tội phạm tài chính và rửa tiền. Bằng cách xác minh chính xác danh tính của khách hàng, các tổ chức tài chính có thể đảm bảo rằng cá nhân là người mà họ tuyên bố, giảm nguy cơ xảy ra các hoạt động gian lận như chiếm đoạt tài khoản, trộm cắp danh tính hoặc sử dụng tiền bất hợp pháp.
- Tuân thủ quy định: Ngành tài chính được quản lý chặt chẽ, với các yêu cầu tuân thủ nghiêm ngặt nhằm ngăn chặn rửa tiền, tài trợ khủng bố và các hoạt động bất hợp pháp khác. Xác minh danh tính mạnh mẽ là điều cần thiết để đáp ứng các nghĩa vụ theo quy định này, vì nó giúp xác định danh tính thực sự của khách hàng và đảm bảo rằng họ không tham gia vào các hoạt động bất hợp pháp.
- Bảo vệ tài sản và dữ liệu của khách hàng: Xác minh danh tính bảo vệ tài sản và dữ liệu của cả khách hàng và tổ chức tài chính. Bằng cách xác nhận danh tính của khách hàng, các tổ chức tài chính có thể ngăn chặn truy cập trái phép vào tài khoản, bảo vệ thông tin tài chính nhạy cảm và duy trì lòng tin của khách hàng.
- Giảm thiểu Rủi ro và Trách nhiệm: Việc không triển khai các biện pháp xác minh danh tính mạnh mẽ có thể khiến các tổ chức tài chính phải chịu những rủi ro và trách nhiệm đáng kể. Nếu các hoạt động gian lận xảy ra do xác minh danh tính không đầy đủ, tổ chức tài chính có thể phải đối mặt với tổn thất tài chính, tổn hại đến danh tiếng, hậu quả pháp lý và các hình phạt theo quy định. Việc triển khai các quy trình xác minh danh tính mạnh mẽ giúp giảm thiểu những rủi ro này.
- Tăng cường lòng tin của khách hàng: Các quy trình xác minh danh tính mạnh mẽ xây dựng lòng tin giữa khách hàng và các tổ chức tài chính. Khi khách hàng cảm thấy tự tin rằng danh tính của họ được xác minh đúng cách, họ có nhiều khả năng tham gia vào các giao dịch tài chính, mở tài khoản và sử dụng các dịch vụ kỹ thuật số. Lòng tin rất quan trọng để thúc đẩy mối quan hệ lâu dài với khách hàng và đảm bảo sự hài lòng của khách hàng.
- Cho phép chuyển đổi số: Ngành tài chính đang trải qua quá trình chuyển đổi số nhanh chóng, với sự phụ thuộc ngày càng tăng vào các dịch vụ ngân hàng trực tuyến và di động. Xác minh danh tính mạnh mẽ là rất quan trọng để cho phép các giao dịch số an toàn và liền mạch. Nó cho phép các tổ chức tài chính cung cấp các dịch vụ thuận tiện trong khi vẫn duy trì các biện pháp bảo mật mạnh mẽ để bảo vệ chống lại gian lận và truy cập trái phép.
- Chống trộm danh tính và chiếm đoạt tài khoản: Trộm danh tính và chiếm đoạt tài khoản gây ra mối đe dọa đáng kể cho cá nhân và tổ chức tài chính. Xác minh danh tính mạnh mẽ giúp phát hiện và ngăn ngừa những sự cố này bằng cách đảm bảo rằng cá nhân đang sử dụng danh tính thực của mình khi truy cập các dịch vụ tài chính hoặc thực hiện giao dịch.
Nhìn chung, xác minh danh tính mạnh mẽ là rất quan trọng trong lĩnh vực tài chính để giảm thiểu rủi ro, tuân thủ các quy định, bảo vệ tài sản và dữ liệu của khách hàng, thúc đẩy lòng tin và cho phép các dịch vụ kỹ thuật số an toàn. Bằng cách triển khai các quy trình xác minh danh tính mạnh mẽ, các tổ chức tài chính có thể tăng cường bảo mật, ngăn ngừa gian lận và duy trì tính toàn vẹn của hoạt động của họ.
Nhận dạng sinh trắc học nào được sử dụng trong lĩnh vực tài chính
Trong lĩnh vực tài chính, nhiều phương pháp nhận dạng sinh trắc học được sử dụng để tăng cường bảo mật và cung cấp xác thực thuận tiện và đáng tin cậy cho khách hàng. Sau đây là một số phương pháp nhận dạng sinh trắc học thường được sử dụng trong lĩnh vực tài chính:
- Nhận dạng vân tay: Phương pháp này bao gồm việc thu thập và phân tích các mẫu duy nhất có trong dấu vân tay của một cá nhân. Máy quét vân tay thường được sử dụng để xác thực người dùng cho nhiều giao dịch tài chính khác nhau, bao gồm cả giao dịch ngân hàng di động và truy cập vào các hệ thống an toàn.
- Nhận dạng mống mắt: Nhận dạng mống mắt bao gồm việc phân tích các mẫu đặc biệt của mống mắt của một cá nhân, là phần có màu của mắt. Máy quét mống mắt được sử dụng để xác minh danh tính của cá nhân trong các tổ chức ngân hàng và tài chính.
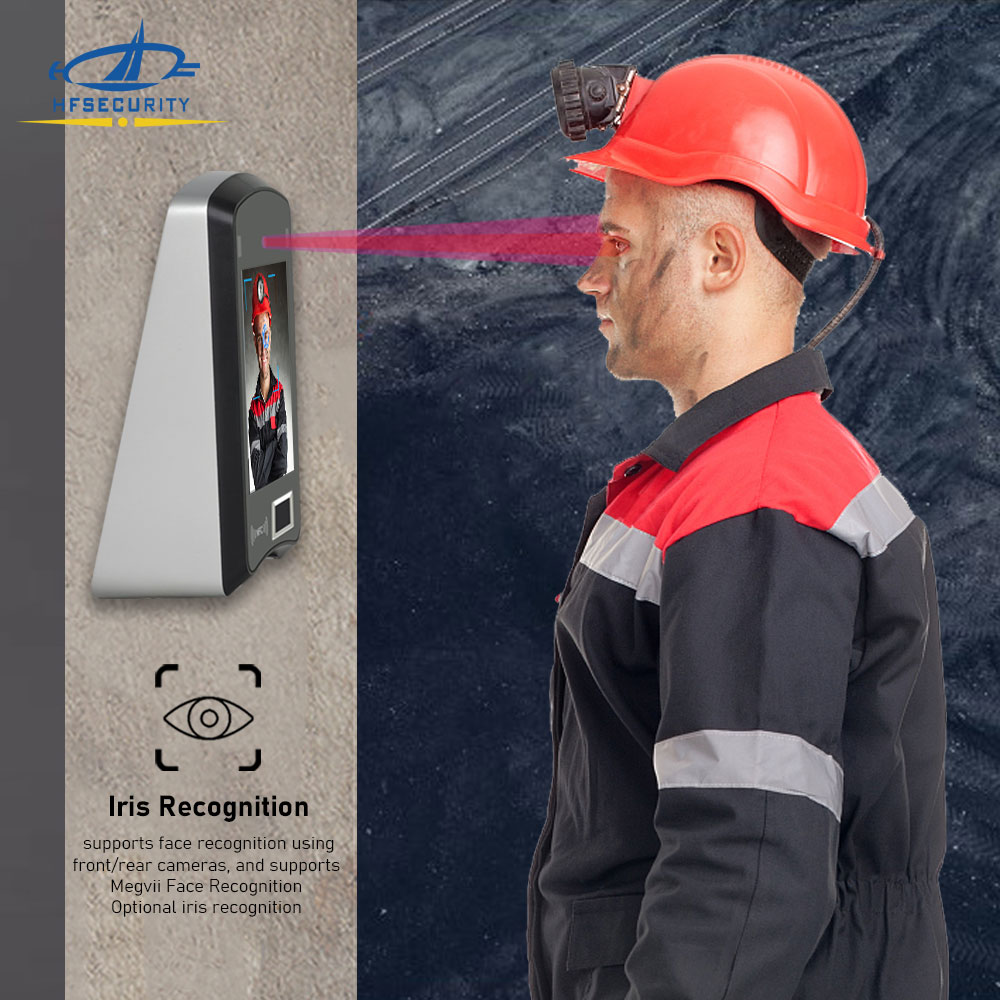

- Nhận dạng khuôn mặt: Công nghệ nhận dạng khuôn mặt sử dụng các đặc điểm khuôn mặt độc đáo để nhận dạng cá nhân. Các tổ chức tài chính có thể sử dụng hệ thống nhận dạng khuôn mặt để xác thực khách hàng trong các giao dịch trực tuyến hoặc tại các chi nhánh.
- Nhận dạng giọng nói: Nhận dạng giọng nói liên quan đến việc phân tích các đặc điểm riêng biệt của giọng nói của một cá nhân, bao gồm cao độ, âm điệu và các đặc điểm giọng nói khác. Nó có thể được sử dụng để xác thực người dùng qua điện thoại hoặc thông qua các ứng dụng hỗ trợ giọng nói cho các giao dịch ngân hàng.
- Nhận dạng tĩnh mạch lòng bàn tay: Phương pháp này ghi lại các mẫu tĩnh mạch độc đáo trong lòng bàn tay của một cá nhân. Máy quét tĩnh mạch lòng bàn tay được sử dụng để xác thực khách hàng tại một số tổ chức tài chính để truy cập an toàn vào tài khoản và giao dịch.
- Sinh trắc học hành vi: Sinh trắc học hành vi phân tích các mẫu duy nhất trong hành vi của một cá nhân, chẳng hạn như nhịp độ gõ, cách sử dụng chuột hoặc các mẫu điều hướng. Các mẫu này có thể được sử dụng để xác thực người dùng trong các giao dịch trực tuyến hoặc truy cập vào hệ thống tài chính.
Cần lưu ý rằng việc áp dụng các phương pháp nhận dạng sinh trắc học có thể khác nhau giữa các tổ chức tài chính khác nhau và một số tổ chức có thể sử dụng kết hợp các công nghệ sinh trắc học này để tăng cường bảo mật. Ngoài ra, những tiến bộ trong công nghệ có thể giới thiệu các phương pháp nhận dạng sinh trắc học mới trong tương lai.
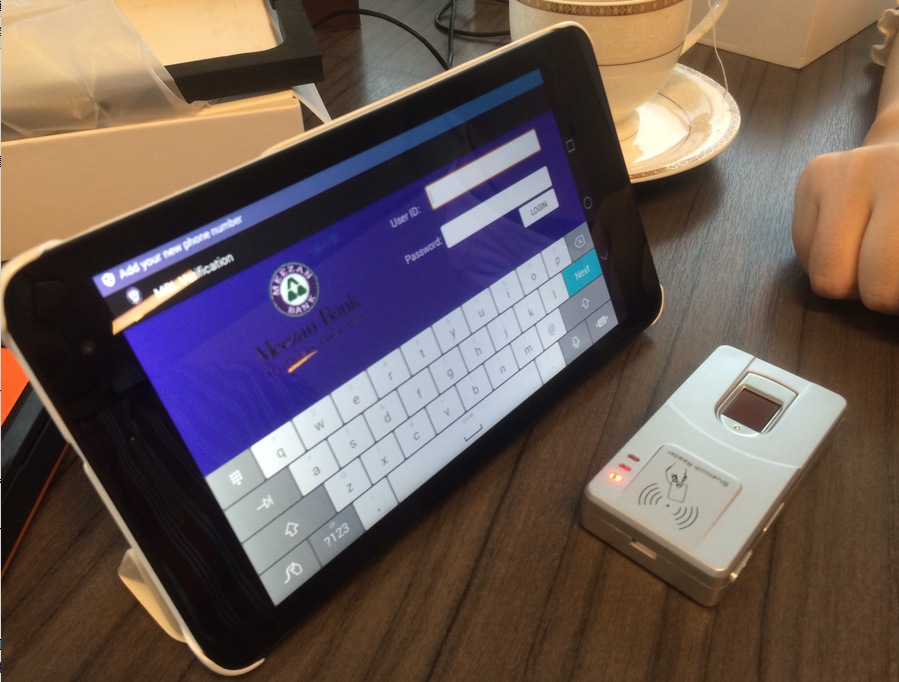
Lợi ích của sinh trắc học trong dịch vụ tài chính
Sinh trắc học trong dịch vụ tài chính mang lại một số lợi ích, bao gồm:
- Bảo mật nâng cao: Nhận dạng sinh trắc học phương pháp cung cấp mức độ bảo mật cao hơn so với các phương pháp truyền thống như mật khẩu hoặc mã PIN. Các đặc điểm sinh trắc học là duy nhất đối với mỗi cá nhân, khiến kẻ gian rất khó sao chép hoặc mạo danh chúng. Điều này giúp bảo vệ chống lại hành vi trộm cắp danh tính, truy cập trái phép và các hoạt động gian lận.
- Xác thực đáng tin cậy: Hệ thống sinh trắc học cung cấp xác thực đáng tin cậy bằng cách sử dụng các đặc điểm vật lý hoặc hành vi khó làm giả. Điều này làm giảm nguy cơ dương tính giả hoặc âm tính giả trong quá trình xác minh danh tính, đảm bảo rằng chỉ những cá nhân được ủy quyền mới có thể truy cập thông tin tài chính nhạy cảm hoặc thực hiện giao dịch.
- Tiện lợi và dễ sử dụng: Các phương pháp nhận dạng sinh trắc học mang lại sự tiện lợi cho khách hàng bằng cách loại bỏ nhu cầu phải nhớ và nhập mật khẩu hoặc mã PIN phức tạp. Người dùng chỉ cần cung cấp các đặc điểm sinh trắc học của mình, chẳng hạn như dấu vân tay hoặc quét khuôn mặt, để xác thực, giúp quá trình này diễn ra nhanh chóng và liền mạch. Điều này cải thiện trải nghiệm chung của người dùng và giảm bớt sự bực bội liên quan đến các phương pháp xác thực truyền thống.
- Phòng ngừa gian lận: Hệ thống sinh trắc học có thể làm giảm đáng kể các trường hợp gian lận trong các dịch vụ tài chính. Vì các đặc điểm sinh trắc học là duy nhất đối với mỗi cá nhân, nên kẻ gian khó có thể truy cập trái phép hoặc thực hiện các giao dịch gian lận. Các phương pháp nhận dạng sinh trắc học có thể phát hiện và ngăn chặn nhiều loại gian lận khác nhau, bao gồm chiếm đoạt tài khoản, đánh cắp danh tính và tấn công lừa đảo.
- Hiệu quả về chi phí: Mặc dù việc triển khai các hệ thống sinh trắc học có thể đòi hỏi khoản đầu tư ban đầu, nhưng cuối cùng chúng có thể giúp các tổ chức tài chính tiết kiệm chi phí. Sinh trắc học loại bỏ nhu cầu về mã thông báo vật lý, chẳng hạn như thẻ thông minh hoặc mã thông báo bảo mật, vốn có thể tốn kém để sản xuất và phân phối. Ngoài ra, xác thực sinh trắc học giúp giảm chi phí liên quan đến việc đặt lại mật khẩu, khóa tài khoản và các vấn đề xác thực người dùng khác.
- Tuân thủ quy định: Nhiều tổ chức tài chính phải tuân thủ các yêu cầu theo quy định, chẳng hạn như các quy định về Biết khách hàng của bạn (KYC) và Chống rửa tiền (AML). Các phương pháp nhận dạng sinh trắc học có thể hỗ trợ đáp ứng các yêu cầu này bằng cách cung cấp xác thực khách hàng mạnh mẽ và đảm bảo tính chính xác của việc xác minh danh tính khách hàng.
Nhìn chung, sinh trắc học trong dịch vụ tài chính cung cấp một phương tiện hiệu quả và hiệu suất để bảo mật tài khoản và giao dịch của khách hàng trong khi vẫn mang lại sự tiện lợi và trải nghiệm người dùng liền mạch. Những lợi ích này góp phần tăng cường sự tin tưởng, giảm gian lận và cải thiện hiệu quả hoạt động trong lĩnh vực tài chính.
Quy trình nhận dạng của hệ thống ngân hàng sinh trắc học
Hệ thống ngân hàng sinh trắc học sử dụng dữ liệu sinh trắc học để xác minh danh tính của cá nhân cho nhiều giao dịch ngân hàng khác nhau. Quy trình nhận dạng thường bao gồm các bước sau:
- Đăng ký: Ban đầu, khách hàng cần đăng ký vào hệ thống ngân hàng sinh trắc học. Trong quá trình đăng ký, khách hàng cung cấp thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu sinh trắc học của mình, chẳng hạn như dấu vân tay, đặc điểm khuôn mặt, mẫu mống mắt hoặc dấu giọng nói. Dữ liệu này được lưu trữ an toàn trong cơ sở dữ liệu của ngân hàng và được liên kết với tài khoản của khách hàng.
- Yêu cầu xác thực: Khi khách hàng muốn thực hiện giao dịch ngân hàng, họ sẽ bắt đầu quy trình bằng cách cung cấp thông tin tài khoản hoặc đưa thẻ ngân hàng vào máy ATM hoặc đầu đọc thẻ. Tại thời điểm này, hệ thống sẽ nhắc khách hàng cung cấp dữ liệu sinh trắc học để xác thực.
- Thu thập dữ liệu sinh trắc học: Khách hàng trình bày dữ liệu sinh trắc học của mình, có thể thay đổi tùy thuộc vào hệ thống được sử dụng. Ví dụ, họ có thể đặt ngón tay của mình trên máy quét dấu vân tay, nhìn vào camera để nhận dạng khuôn mặt hoặc nói vào micrô để nhận dạng giọng nói. Hệ thống thu thập dữ liệu sinh trắc học do khách hàng cung cấp.
- Xử lý dữ liệu sinh trắc học: Dữ liệu sinh trắc học thu thập được sẽ được xử lý bởi hệ thống ngân hàng sinh trắc học. Quá trình này bao gồm việc so sánh dữ liệu được cung cấp với mẫu sinh trắc học đã đăng ký được lưu trữ trong cơ sở dữ liệu của hệ thống. Hệ thống sử dụng các thuật toán phức tạp để phân tích dữ liệu thu thập được và xác định tính tương đồng hoặc khớp với mẫu đã lưu trữ.
- Quyết định xác thực: Dựa trên kết quả so sánh, hệ thống đưa ra quyết định xác thực. Nếu dữ liệu sinh trắc học thu thập được khớp chặt với mẫu đã đăng ký, danh tính của khách hàng sẽ được xác minh và họ được cấp quyền truy cập vào tài khoản của mình cho giao dịch được yêu cầu. Nếu không khớp chặt hoặc hệ thống phát hiện ra sự không nhất quán, xác thực có thể không thành công và quyền truy cập vào tài khoản có thể bị từ chối.
- Xử lý giao dịch: Nếu xác thực thành công, giao dịch ngân hàng sẽ tiến hành theo yêu cầu. Khách hàng có thể thực hiện nhiều hoạt động khác nhau như rút tiền mặt, gửi tiền, chuyển tiền hoặc truy cập thông tin tài khoản.
Điều quan trọng cần lưu ý là việc triển khai cụ thể các hệ thống ngân hàng sinh trắc học có thể khác nhau giữa các ngân hàng và quốc gia. Các phương thức sinh trắc học được sử dụng, mức độ biện pháp bảo mật và các thuật toán cụ thể được sử dụng có thể khác nhau, nhưng quy trình chung được nêu ở trên cung cấp một khuôn khổ chung để hiểu quy trình nhận dạng trong các hệ thống ngân hàng sinh trắc học.
Tóm tắt Giải pháp sinh trắc học cho ngân hàng
Các giải pháp sinh trắc học dành cho ngân hàng cung cấp các phương pháp nhận dạng và xác thực tiên tiến bằng cách sử dụng các đặc điểm vật lý hoặc hành vi độc đáo của cá nhân. Các giải pháp này tăng cường bảo mật, giảm gian lận và cung cấp trải nghiệm ngân hàng liền mạch. Sau đây là tóm tắt về các giải pháp sinh trắc học được sử dụng trong ngân hàng:
- Nhận dạng vân tay: Phương thức sinh trắc học này thu thập và phân tích các mẫu vân tay để xác minh danh tính của khách hàng. Máy quét vân tay thường được tích hợp vào máy ATM, thiết bị di động hoặc đầu đọc sinh trắc học chuyên dụng.
- Nhận dạng khuôn mặt: Công nghệ nhận dạng khuôn mặt phân tích các đặc điểm trên khuôn mặt, chẳng hạn như vị trí của mắt, mũi và miệng, để xác minh danh tính. Khách hàng có thể xác thực bản thân bằng cách chụp ảnh tự sướng hoặc nhìn vào camera.
- Nhận dạng mống mắt: Công nghệ nhận dạng mống mắt quét các mẫu độc đáo trong mống mắt. Nó cung cấp độ chính xác cao và thường được sử dụng trong các hệ thống kiểm soát truy cập an toàn trong ngân hàng.
- Nhận dạng giọng nói: Sinh trắc học giọng nói phân tích các mẫu giọng nói, cao độ và các đặc điểm giọng nói khác để xác thực cá nhân. Khách hàng có thể nói cụm mật khẩu hoặc trả lời các câu hỏi bảo mật để xác minh danh tính của họ.
- Nhận dạng tĩnh mạch lòng bàn tay: Công nghệ này sử dụng ánh sáng cận hồng ngoại để quét các mẫu tĩnh mạch trong lòng bàn tay của một người. Nó cung cấp giải pháp sinh trắc học không tiếp xúc và cực kỳ an toàn cho các giao dịch ngân hàng.
- Sinh trắc học đa phương thức: Một số ngân hàng kết hợp nhiều phương thức sinh trắc học để tăng cường bảo mật và cải thiện độ chính xác. Ví dụ, một hệ thống có thể sử dụng cả nhận dạng vân tay và khuôn mặt cho quy trình xác thực hai yếu tố.
Lợi ích của giải pháp sinh trắc học dành cho ngân hàng:
- Tăng cường bảo mật: Sinh trắc học cung cấp phương pháp nhận dạng có độ bảo mật cao vì chúng dựa trên các đặc điểm sinh học độc đáo, khó có thể sao chép.
- Giảm gian lận: Các giải pháp sinh trắc học giúp chống gian lận bằng cách gây khó khăn cực độ cho kẻ mạo danh trong việc bắt chước hoặc làm giả các đặc điểm sinh trắc học.
- Sự tiện lợi và hiệu quả: Xác thực sinh trắc học loại bỏ nhu cầu sử dụng mật khẩu hoặc mã PIN, mang đến trải nghiệm giao dịch ngân hàng nhanh hơn và thuận tiện hơn cho khách hàng.
- Tích hợp liền mạch: Các giải pháp sinh trắc học có thể được tích hợp liền mạch vào các hệ thống ngân hàng hiện có, chẳng hạn như ATM, ứng dụng di động hoặc nền tảng trực tuyến.
- Cải thiện trải nghiệm của khách hàng: Công nghệ sinh trắc học đơn giản hóa quy trình xác thực, giảm khả năng quên mật khẩu hoặc mất thẻ, do đó nâng cao sự hài lòng của khách hàng.
- Tiêu chuẩn tuân thủ và quy định: Các giải pháp sinh trắc học giúp các ngân hàng tuân thủ các quy định về bảo mật và quyền riêng tư bằng cách cung cấp cơ chế xác thực và nhận dạng mạnh mẽ.
Nhìn chung, các giải pháp sinh trắc học cung cấp cho các ngân hàng một phương pháp đáng tin cậy và an toàn để xác minh danh tính khách hàng, giảm gian lận và mang lại trải nghiệm ngân hàng liền mạch và thuận tiện.

