Facial recognition and fingerprint recognition are two different biometric identification methods. This article will compare them from the perspective of definition, process, and performance.
Define face recognition &Fingerprint Recognition
Whether it is facial recognition or fingerprint recognition, the main purpose is to prove who you are, or whether you are you.
Face recognition:
As the name suggests, facial recognition recognizes facial information. Facial recognition is to obtain your facial information through a camera, which may be a video stream or a video, and then use facial recognition algorithms to process the unprocessed source files.
Fingerprint recognition
Fingerprint recognition recognizes your fingerprint information. Fingerprint recognition can be done through capacitive sensors or data information, or through optical imaging technology, taking photos or your fingerprint pictures, and then using fingerprint algorithms to process your fingerprint images to generate feature templates that belong only to you.
How do they work?
face recognition:
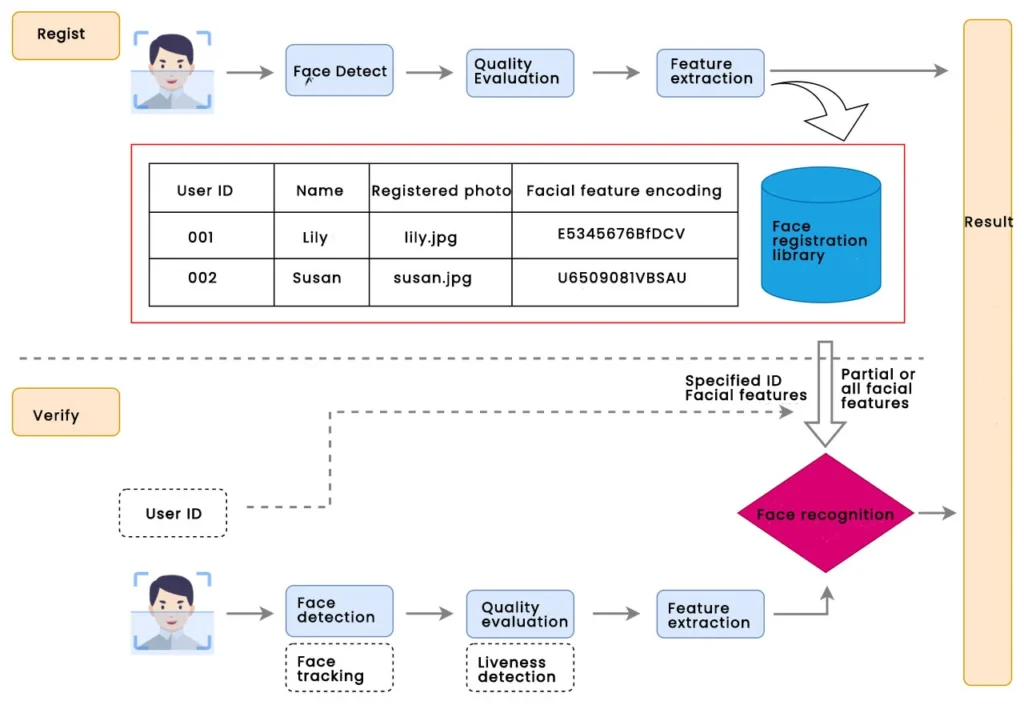
The process of facial recognition is divided into three parts: face registration, feature template generation, and person recognition;
You can refer to the following working process
The camera obtains your facial information, and analyzes it according to the feature algorithm to form your feature image. This is your unique identification factor. The system will identify and filter your feature information in the database
Fingerprint recognition:
Fingerprint recognition is divided into three processes: fingerprint registration, feature template image, and fingerprint comparison. Fingerprint registration is also called fingerprint registration. The fingerprint image is obtained through the fingerprint device, and the feature information is extracted using the feature value algorithm to form a fingerprint feature template. Use the feature template to find your information in the database

Accuraccy
Before understanding accuracy, you need to understand several key terms;
False Acceptance Rate (FAR): False Acceptance Rate. Explanation: The probability that the system mistakenly matches your information with someone else’s information;
False Rejection Rate (FRR): The probability that the system mistakenly rejects legitimate user information
Equal Error Rate (EER): Equal Error Rate. FAR is equal to FRR, which is generally used as an indicator for overall correctness considerations.
| Face Recognition | Fingerprint Recognition | |
| EER | 0.1%~1% | 0.001%~0.1 |
| FRR | 1%~5% | 1%~5% |
| FAR | <0.01% | <0.001% |
Features Table
| Face | Fingerprint | |
| Identification method | Non-contact identification | Contact identification |
| Hygiene | Non-contact identification, reduces the risk of cross infection | Contact identification, has the risk of cross infection |
| Environmental impact | Lighting, angle, facial occlusion factors, the recognition effect will be affected | Dry, wet fingers, fingerprint incomplete and other factors will affect the fingerprint recognition effect |
| Cost | Equipment, maintenance costs are relatively high | Cost is relatively low |
| User preference | High | Medium |
| Convenience | High | Slightly cumbersome |
| Recognition speed | (Comparison of this type) 2-5S | Comparison of this type 3~5 seconds |
| Privacy and security | Same | Same |
| Market share | 40% | >50% |
Common use cases
Whether it is fingerprint recognition or facial recognition, both need to focus on the use scenario. Here are some of your sharing;
Fingerprints are generally used for identity authentication and personal information recognition, while facial recognition is usually used for monitoring and payment;
Fingerprint Recognition
Access control system: office buildings, secure areas, government equipment
Financial system: ATM, KYC
Criminal identification: law enforcement fingerprint database
Facial Recognition
Monitoring system: airports, public places;
Access control identity verification: border, government access control
Retail stores: face payment
Future
Fingerprint and facial recognition each have their own unique features. In the future, more use scenarios will coexist with the two systems to give full play to their stronger advantages.
Follow HFSECURITY to provide you with more biometric scenario solutions

